Sarcopenia in older adults stems from muscle fiber atrophy, hormonal changes, and declining mitochondrial function, all leading to weaker muscles. Sedentary lifestyles and poor nutrition further accelerate muscle loss, while diminished nerve signals impair muscle activation. Resistance training, focusing on safe, progressive exercises 2-3 times weekly, helps rebuild strength. Incorporating proper nutrition, lifestyle adjustments, and expert guidance can make a significant difference—continue exploring ways to effectively combat this condition and stay active longer.
Key Takeaways
- Sarcopenia results from muscle fiber atrophy, neuromuscular decline, hormonal changes, and reduced mitochondrial function in aging adults.
- Adequate nutrition, especially protein and vitamin D intake, is essential to support muscle maintenance and slow sarcopenia progression.
- Resistance training programs for seniors should focus on safe, progressive exercises 2-3 times weekly with proper technique.
- Incorporating lifestyle modifications like staying active, managing stress, and improving sleep enhances muscle health and resistance to sarcopenia.
- Supplementation with nutrients and herbal remedies can support muscle recovery, but should be combined with appropriate resistance training.
Understanding the Development of Sarcopenia in Older Adults

As people age, their muscles naturally begin to decline in size and strength, leading to sarcopenia. This process involves muscle fiber atrophy, where the muscle fibers shrink and weaken over time. You’ll notice this as reduced muscle mass and decreased power. Neuromuscular decline also plays a significant role; as the communication between nerves and muscles deteriorates, your ability to activate muscles effectively diminishes. This weakening of the neuromuscular system further accelerates muscle loss and impacts your coordination and balance. The combination of muscle fiber atrophy and neuromuscular decline creates a cycle that worsens with age if not addressed. Understanding these mechanisms helps you recognize the importance of early interventions to slow down or mitigate sarcopenia’s effects. Additionally, muscle regeneration capacity diminishes with age, making it even more crucial to engage in resistance training to maintain muscle health and prevent further decline. The decline in power output associated with aging also underscores the need for targeted exercise programs. Recognizing the age-related changes in muscle tissue can guide effective strategies for intervention and preservation of function.
Hormonal and Metabolic Contributors to Muscle Loss

As you age, your hormonal levels decline, which can directly lead to muscle loss. Additionally, your metabolic rate slows down, making it harder to maintain muscle mass. Understanding how these changes affect your body is key to addressing sarcopenia effectively. Implementing resistance training protocols can help counteract these age-related declines and promote muscle preservation. Regular physical activity can also support metabolic health, further aiding in the prevention of muscle deterioration. For example, top beaches often host outdoor fitness classes that can be beneficial for maintaining muscle strength and overall health.
Hormonal Decline Impact
Hormonal decline plays a significant role in the development of sarcopenia by disrupting the balance of muscle maintenance processes. As you age, hormonal fluctuations reduce levels of key hormones like testosterone, growth hormone, and estrogen, which are essential for muscle synthesis and repair. This decline weakens your body’s ability to rebuild muscle tissue, accelerating muscle loss. Endocrine therapies can sometimes help counteract these effects, but they aren’t always suitable for everyone. Understanding how hormonal changes impact muscle health allows you to adopt targeted strategies, such as resistance training, to stimulate hormone production naturally. Recognizing the influence of hormonal decline empowers you to take proactive steps to preserve muscle mass and combat sarcopenia effectively.
Metabolic Rate Changes
Changes in metabolic rate markedly influence muscle loss during aging, often working alongside hormonal declines to accelerate sarcopenia. As your metabolic rate decreases, your energy expenditure drops, making it harder to maintain muscle mass. This slowdown impacts your body’s ability to repair and build muscle tissue effectively. Key factors include:
- Reduced basal metabolic rate (BMR), leading to lower calorie burn at rest.
- Declined physical activity, further decreasing energy expenditure.
- Altered mitochondrial function, impairing energy production in muscle cells.
- The use of trendy dog sweaters as a metaphor for how external factors can influence internal health, highlighting the importance of proactive measures. Additionally, understanding how metabolic contributors interact with hormonal changes can help tailor effective resistance training protocols. Recognizing the significance of energy expenditure in muscle preservation emphasizes the need for targeted interventions to counteract these metabolic shifts. Moreover, emerging research underscores the role of nutritional strategies in supporting metabolic health and muscle maintenance as you age.
These metabolic shifts contribute to muscle wasting by limiting the energy available for muscle maintenance and regeneration. Understanding these changes helps you target strategies—like resistance training—to counteract declining metabolic rate and preserve muscle health as you age.
The Role of Physical Activity and Sedentary Lifestyle

Physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle mass and strength as you age, helping to combat sarcopenia. When you engage in regular exercise, you counteract sedentary behavior and physical inactivity, which are major risk factors for muscle loss. Sitting for prolonged periods reduces muscle stimulation, leading to weakness and atrophy. Staying active encourages muscle protein synthesis and preserves functional capacity. Even light activities, like walking or stretching, can make a difference in preventing muscle deterioration. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle accelerates sarcopenia by diminishing the stimuli needed for muscle maintenance. To protect your muscle health, aim for consistent physical activity—incorporate strength training, aerobic exercises, and movement throughout the day to stay active and healthy as you age. Regular movement not only boosts overall health but also positively impacts exercise performance and recovery. Incorporating regular physical activity can also help improve muscle protein synthesis, which is essential for maintaining muscle mass in older adults. Additionally, engaging in varied forms of activity can enhance overall muscle endurance and reduce the risk of falls and injuries. Furthermore, staying physically active supports metabolic health, which is linked to muscle preservation and overall well-being.
Nutritional Factors Influencing Muscle Health
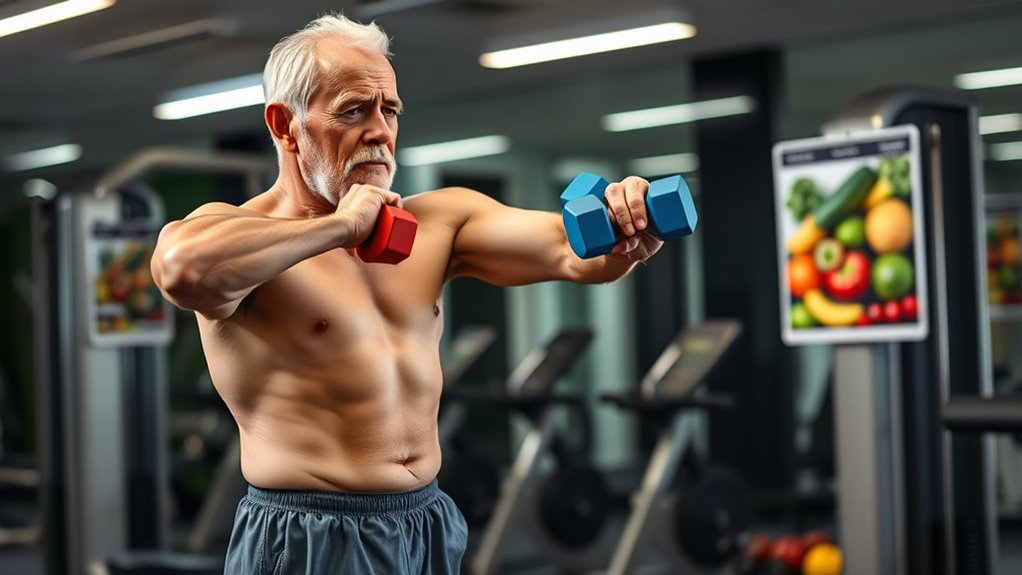

Maintaining muscle health as you age depends not only on staying active but also on paying attention to your diet. Proper nutrition plays a pivotal role in preventing sarcopenia. Focus on:
Prioritize balanced nutrition with protein, vitamin D, and nutrient-dense foods to preserve muscle health as you age.
- Increasing protein intake to support muscle repair and growth, aiming for sources like lean meats, dairy, or plant-based options. Incorporating adequate nutrient intake can further enhance muscle preservation efforts.
- Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels, which help improve muscle strength and reduce fall risks.
- Incorporating nutrient-dense foods to provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall muscle function. Using brewing techniques such as proper water temperature and timing can optimize nutrient extraction from foods.
- Including plant-based omega-3s like chia seeds, which can contribute to reducing inflammation and supporting muscle recovery.
Neglecting these factors can accelerate muscle loss and weaken your mobility. Make sure your diet is balanced and rich in these key nutrients to maintain muscle health and enhance the benefits of resistance training. Proper nutrition complements your active efforts to combat sarcopenia effectively.
Designing Effective Resistance Training Programs for Seniors
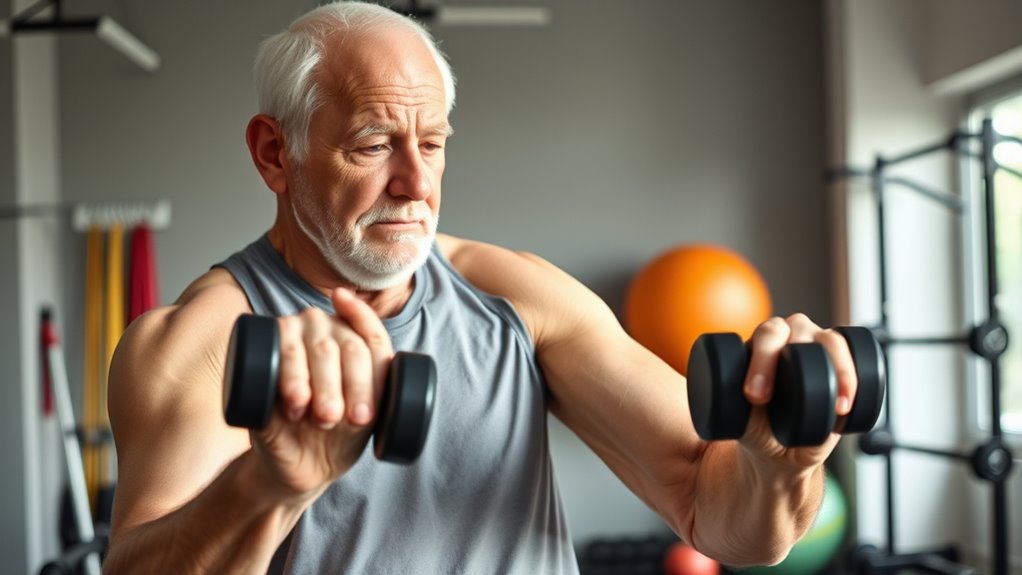

Designing an effective resistance training program for seniors requires selecting safe, appropriate exercises that promote muscle strength without risking injury. Focus on exercises that stimulate muscle hypertrophy, such as compound movements and resistance-based activities, while maintaining proper form. To maximize benefits, set a consistent exercise frequency—aim for 2 to 3 sessions per week—to allow muscles adequate recovery and growth. Incorporate progressive overload gradually to challenge muscles without overtraining. Use lighter weights or resistance bands initially, increasing intensity as strength improves. Prioritize full-body routines to ensure balanced muscle development. Remember, the goal is to enhance muscle mass and functional capacity safely, so customize your program to your ability level and gradually build intensity over time. Proper form is essential to prevent injury and ensure effective workouts. Additionally, incorporating exfoliation through glycolic acid can help improve skin texture and health, supporting overall well-being during training routines. Engaging in holistic development approaches, including balanced nutrition and adequate rest, can further optimize muscle growth and recovery.
By understanding and managing potential risks, such as injury prevention, you can develop a sustainable and effective resistance training routine for seniors.
Safety Considerations and Progression in Resistance Exercises
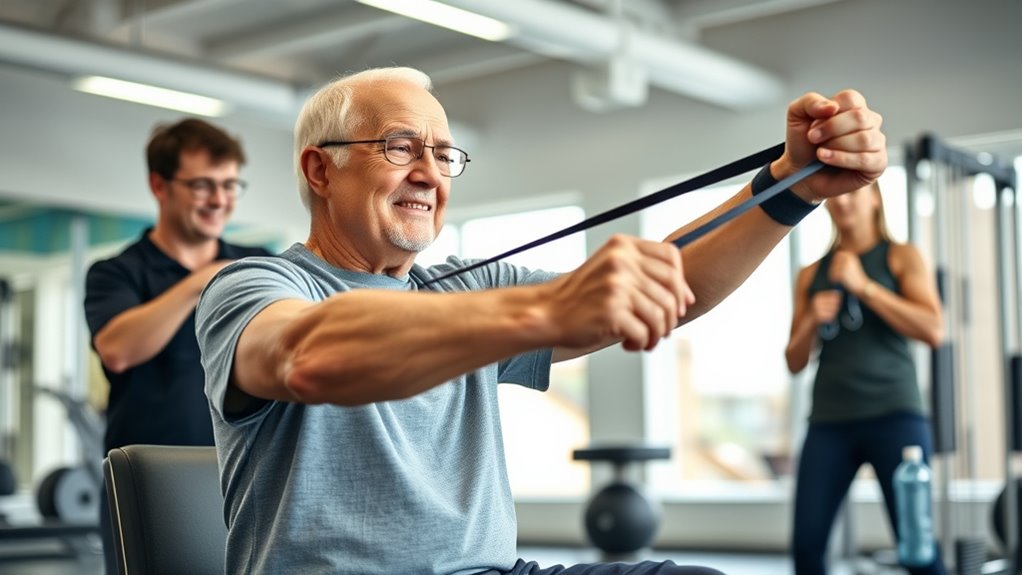

Ensuring safety during resistance exercises is essential, especially for older adults, to prevent injuries and encourage consistent participation. Focus on these key aspects:
Prioritize proper technique, gradual progress, and correct equipment setup to keep older adults safe during resistance exercises.
- Master proper technique before increasing weight or intensity.
- Progress gradually, listening to your body’s signals.
- Use appropriate equipment and confirm proper setup for stability.
- Incorporate celebrity lifestyle insights to stay motivated and make workouts more engaging.
- Regularly assess your muscle strength and endurance to tailor your exercise progression safely.
Additional Strategies to Support Muscle Preservation
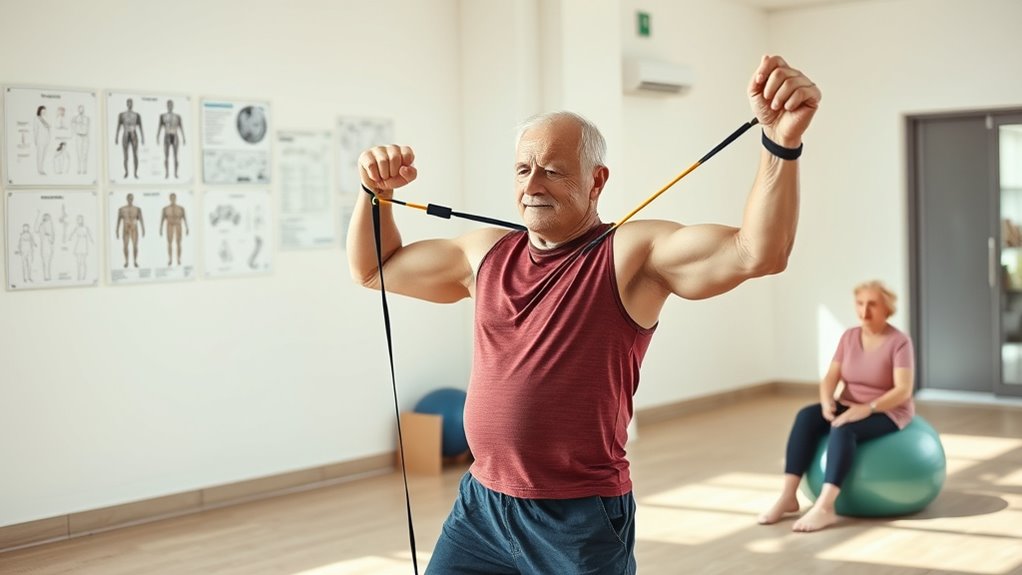

To effectively support muscle preservation, you should consider optimizing your nutrition, making positive lifestyle changes, and exploring supplementation options. These strategies can complement your exercise routine and help maintain muscle mass as you age. Together, they form an all-encompassing approach to preserving strength and mobility.
Nutritional Optimization Strategies
Optimizing your nutrition is essential for supporting muscle preservation as you age. Proper nutrition enhances muscle maintenance and helps combat sarcopenia. Focus on these key strategies:
- Prioritize dietary protein intake—aim for about 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight daily to stimulate muscle synthesis.
- Ensure adequate micronutrient intake, especially vitamin D, calcium, and antioxidants, to support muscle function and overall health.
- Balance your meals with nutrient-dense foods to maximize nutrient absorption and prevent deficiencies.
Lifestyle Habit Modifications
Implementing simple lifestyle habit modifications can considerably support muscle preservation as you age. Prioritize stress management by practicing mindfulness, deep breathing, or engaging in relaxing activities to reduce cortisol levels that may accelerate muscle loss. Adopting good sleep hygiene is equally important; aim for consistent sleep schedules, avoid screens before bed, and create a comfortable sleeping environment. Quality sleep promotes muscle recovery and overall health. Additionally, managing stress helps prevent hormonal imbalances that contribute to sarcopenia. These small changes can enhance your body’s ability to maintain muscle mass, complement resistance training, and improve your overall well-being. Focus on establishing routines that incorporate stress reduction and sleep optimization, and you’ll support your efforts to preserve muscle strength as you age.
Supplementation and Support
Building on lifestyle habits, incorporating targeted supplementation can further support muscle preservation as you age. Consider these strategies:
- Use antioxidant supplements like vitamin C and E to combat oxidative stress that accelerates muscle loss.
- Explore herbal remedies such as ginseng or turmeric, which may reduce inflammation and improve muscle function.
- Supplement with protein powders or amino acids to ensure adequate nutrient intake for muscle repair and growth.
These additions can enhance your resistance training efforts and promote muscle health. While supplements aren’t a substitute for exercise, they provide extra support, especially if your diet is lacking. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting new supplements, especially herbal remedies, to ensure safety and proper dosage. Combining lifestyle, training, and targeted support offers the best chance to combat sarcopenia.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Genetics Influence Sarcopenia Development in Older Adults?
Genetics play a role in how you develop sarcopenia by influencing your genetic predisposition and inherited muscle traits. If your family has a history of muscle loss or weakness, you might be more susceptible. These genetic factors can affect your muscle mass, strength, and recovery ability. Understanding your genetic background helps you realize the importance of tailored resistance training to combat muscle degeneration effectively.
Can Mental Health Impact Muscle Loss and Recovery Strategies?
You might think mental health only affects mood, but it also impacts muscle recovery. When you’re stressed or anxious, your body releases hormones like cortisol that can accelerate muscle loss. Prioritizing mental health through stress management and therapy can improve muscle recovery, helping you maintain strength longer. Addressing mental health isn’t just about emotional well-being; it’s a crucial part of overall health and muscle preservation.
What Are the Best Ways to Motivate Elderly Individuals to Stick to Resistance Training?
You can keep elderly individuals motivated to stick to resistance training by emphasizing social support and clear goal setting. Encourage them to exercise with friends or join group classes, making workouts more enjoyable and social. Help them set realistic, achievable goals to track progress, boosting confidence and commitment. When they see progress and feel supported, they’re more likely to stay consistent and enjoy the benefits of resistance training.
How Do Medications Affect Muscle Health and Training Outcomes?
Medications act like double-edged swords, impacting muscle health in complex ways. You need to be aware of medication side effects, such as fatigue or weakness, which can hinder your training progress. Drug interactions might also interfere with muscle recovery or impair your response to resistance exercises. Always consult your healthcare provider to understand how your medications could influence your muscle strength, ensuring safe and effective training outcomes.
Are There Specific Recovery Protocols After Resistance Training for Seniors?
After resistance training, you should focus on proper recovery protocols. Prioritize post-exercise nutrition rich in protein to support muscle repair, and verify you get quality sleep, which boosts recovery and reduces soreness. Incorporate rest days and gentle stretching to prevent injury. These steps help older adults recover effectively, maintain muscle health, and enhance training outcomes, making sure you’re progressing safely and sustainably.
Conclusion
As you embrace resistance training, imagine your muscles awakening like a sunrise, strong and vibrant. Each session builds resilience, fueling your confidence and essentiality. With mindful movement and balanced nutrition, you nurture a future where strength flows smoothly through your daily life. Keep progressing, stay consistent, and let your body tell a story of resilience and renewal. Your journey toward preserved muscle and renewed energy begins with each deliberate, empowering choice.