Uterine fibroids are benign tumors influenced by hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental toxins, which disrupt your hormonal balance and promote growth. They involve cellular proliferation and dense extracellular matrices, causing symptoms like heavy bleeding and pressure that affect daily life. Non-surgical options like medications, minimally invasive procedures, and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and preserve fertility. To learn more about how these factors and treatments work together, explore further details below.
Key Takeaways
- Uterine fibroids are growths influenced by hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental toxins, which stimulate cell proliferation and extracellular matrix buildup.
- Non-surgical treatments include medications, uterine artery embolization, and minimally invasive procedures tailored to preserve fertility.
- Accurate diagnosis often involves ultrasound, MRI, and biopsy to guide personalized, less invasive management options.
- Lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise, and stress reduction can help manage symptoms and reduce fibroid growth.
- Emerging therapies focus on targeted pharmacologic agents and biomarkers to offer effective, fertility-preserving alternatives.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids: An Overview
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus, affecting many women during their reproductive years. Though their exact cause isn’t fully understood, lifestyle choices can influence symptoms. Making diet modifications, like reducing red meat and increasing fruits and vegetables, may help manage fibroid growth. Regular exercise routines support overall health and can reduce inflammation, potentially easing symptoms. Staying active helps maintain a healthy weight, which is linked to lower fibroid risk. Incorporating natural materials like wood and linen into your environment may also promote overall well-being. While these changes don’t cure fibroids, they empower you to take control of your health. Combining a balanced diet with consistent physical activity can contribute to symptom management and improve your quality of life. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Factors Contributing to Fibroid Development

While the exact cause of fibroid development remains unknown, several factors are known to contribute to their growth. Hormonal fluctuations, especially estrogen and progesterone levels, play a significant role by stimulating uterine tissue growth. You might notice fibroids often enlarge during pregnancy or with hormonal therapies. Environmental toxins also influence fibroid development; exposure to substances like pesticides, plastics, and pollutants can disrupt your hormonal balance, potentially promoting fibroid growth. These toxins may interfere with your body’s natural hormone regulation, creating an environment conducive to fibroid formation. Additionally, studies suggest that airless paint sprayers have minimal impact on indoor air quality compared to traditional painting methods, which may be relevant when considering indoor air quality and environmental toxin exposure. Environmental toxins can also affect the body’s hormonal balance, further increasing the risk of fibroid development. While genetics and hormones also matter, understanding how hormonal fluctuations and environmental toxins impact your body helps you recognize risk factors and consider lifestyle adjustments to support uterine health.
Genetic and Hormonal Influences
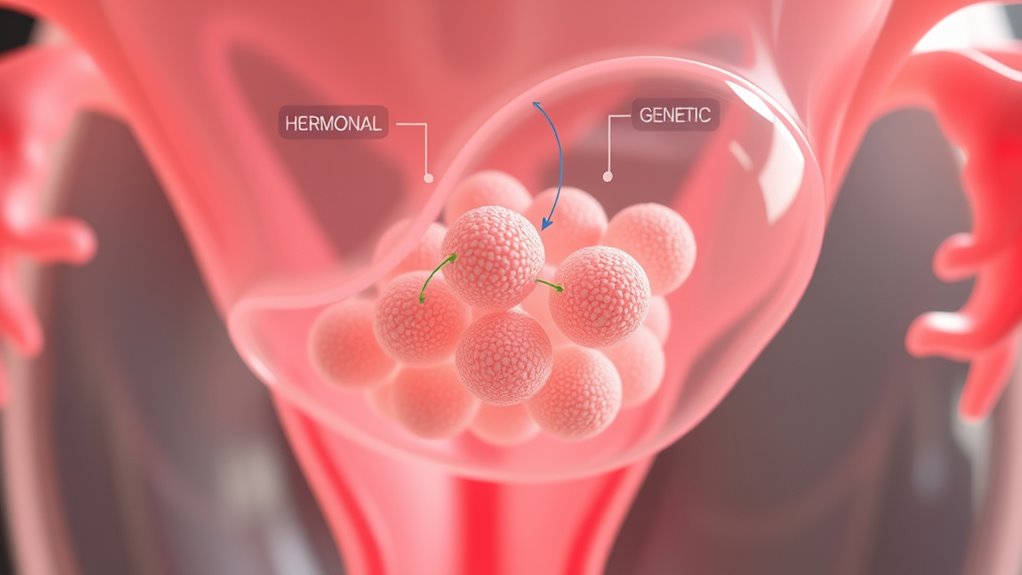
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of fibroids, with research showing that women with a family history are more likely to develop them. Specific genetic mutations can predispose you to fibroid formation by altering normal cell growth regulation. These mutations often affect genes involved in cellular proliferation and tissue growth. Hormonal regulation also influences fibroid development, as estrogen and progesterone promote fibroid growth by stimulating cellular activity in the uterine muscles. Fluctuations in these hormones can cause fibroids to enlarge or shrink, impacting symptoms. Both genetic mutations and hormonal regulation interact to increase the risk of fibroids, making it essential to contemplate your family history and hormonal balance when evaluating your risk factors. Additionally, understanding the genetic and hormonal influences can help in developing targeted non-surgical treatment strategies.
Cellular and Molecular Changes in Fibroids
Cellular and molecular changes within fibroids involve complex alterations that drive their growth and development. You’ll see increased fibroid cell proliferation, which means more cells are dividing rapidly, contributing to the tumor’s expansion. At the same time, the extracellular matrix, a network of proteins and fibers surrounding the cells, becomes abnormally abundant and dense. This buildup of extracellular matrix not only provides structural support but also promotes further cell growth and fibroid stiffness. These changes are influenced by hormonal signals and genetic factors, but the core process involves a shift in cellular behavior and extracellular environment. Additionally, the role of hormonal regulation is critical in modulating these cellular and molecular alterations. Understanding these molecular alterations helps explain why fibroids grow and persist, and it highlights potential targets for non-surgical treatments aimed at disrupting these cellular processes. Recent research also emphasizes the importance of cell signaling pathways in mediating these changes and offers promising avenues for targeted therapies. Furthermore, advances in molecular biology techniques have improved our understanding of fibroid pathogenesis, paving the way for novel therapeutic options.
How Fibroids Grow and Change Over Time
The cellular and molecular changes within fibroids set the stage for their growth over time, influenced by hormonal fluctuations and ongoing genetic factors. As estrogen and progesterone levels rise and fall, they stimulate fibroid cells to multiply and produce more extracellular matrix, fueling fibroid growth. Hormonal fluctuations during your menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause can cause fibroids to expand or shrink. Genetic mutations also play a role, affecting cell behavior and promoting abnormal growth patterns. Over time, these combined factors lead to significant changes in size and shape. You might notice fibroids growing gradually or suddenly enlarging during hormonal shifts. Understanding how fibroids evolve helps explain their unpredictable growth patterns and underscores the importance of monitoring changes over time. Additionally, hormonal influences such as fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone are crucial in driving changes in fibroid size and activity. External factors like environmental exposures may also impact fibroid development and progression. Research indicates that hormonal fluctuations can be affected by lifestyle and environmental factors, further complicating fibroid growth dynamics.
Symptoms and Impact on Daily Life

You might notice symptoms like heavy bleeding, pelvic pressure, or discomfort that can disrupt your daily routines. These issues can make simple tasks feel more challenging and affect your overall quality of life. Additionally, dealing with ongoing symptoms may take an emotional toll, impacting your well-being and peace of mind. Recognizing the importance of support and guidance can help manage these challenges more effectively. Understanding the pathogenesis of fibroids can also offer insight into potential treatment options and long-term management strategies. Being aware of symptoms of breast cancer can aid in early detection and prompt medical consultation, which is essential for effective treatment.
Common Symptom Manifestations
Uterine fibroids often cause a range of symptoms that can substantially disrupt daily life. You might experience heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, or lower back pain, affecting your routine. These symptoms can lead to fatigue and anemia, making daily tasks more challenging. Managing symptoms could involve diet modifications and tailored exercise routines to alleviate discomfort. You may notice urinary frequency or constipation, impacting your comfort and focus. Additionally, understanding underlying causes, such as fibroid growth mechanisms, can help in exploring targeted treatment options.
Daily Life Challenges
Many symptoms caused by uterine fibroids can considerably interfere with your daily routines. Heavy bleeding, cramping, and fatigue often make simple tasks more challenging. You might find yourself adjusting your diet, avoiding certain foods that worsen bloating or discomfort. Incorporating diet modifications can help manage symptoms and boost your energy. Additionally, fibroids can limit your exercise routines, as pain or heaviness may discourage physical activity. You may need to modify or reduce intense workouts, opting instead for gentle exercises like walking or stretching. These adjustments can help you stay active without exacerbating symptoms. Furthermore, understanding the impact of hormonal imbalances related to fibroids can aid in managing your condition more effectively. Recognizing the role of cultural celebrations can also provide emotional support during challenging times. Overall, uterine fibroids can significantly impact your daily life, requiring you to adapt your habits to maintain comfort and well-being. For example, understanding cookies can help you manage your online privacy preferences and improve your overall browsing experience.
Emotional Well-being Effects
Living with uterine fibroids can take a toll on your emotional health, as persistent symptoms often lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or sadness. These emotional challenges can affect your daily life, making it harder to stay positive. Practicing mindfulness meditation helps you manage stress and build emotional resilience, supporting your mental well-being. Recognizing your emotional responses is key to coping effectively. Here’s a quick overview:
| Emotional Impact | Strategies to Cope |
|---|---|
| Anxiety about health | Practice mindfulness meditation |
| Frustration with symptoms | Focus on emotional resilience |
| Sadness or depression | Seek support and stay active |
| Stress from daily challenges | Maintain a positive outlook |
Taking small steps can improve your emotional well-being despite fibroids. Incorporating effective track development techniques can also help in managing emotional stress associated with chronic health conditions. Additionally, understanding the pathogenesis of fibroids can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as aromatherapy with essential oils may further support your emotional balance.
Diagnostic Techniques for Detecting Fibroids
How can healthcare providers accurately identify fibroids early on? The answer lies in effective diagnostic techniques. Imaging modalities, such as ultrasound, are often the first step, providing clear images of the uterus and detecting fibroids’ size and location. MRI may be used for more detailed visualization if needed. In some cases, biopsy procedures are performed to rule out other conditions or confirm diagnosis, especially if atypical features are present. These procedures help guarantee accurate detection and assessment of fibroids. Early identification allows you to explore appropriate management options sooner. Remember, combining imaging techniques with biopsy procedures offers a thorough approach to diagnosing fibroids accurately, ultimately guiding effective treatment plans tailored to your needs.
Non‑Surgical Treatment Options and Their Benefits
When it comes to managing uterine fibroids, non-surgical treatment options can offer effective relief without the need for invasive procedures. These approaches focus on improving your quality of life through lifestyle adjustments and medical therapies. You might consider diet modifications that reduce inflammation and support hormonal balance, helping to shrink fibroids over time. Incorporating regular exercise routines can also manage symptoms by improving circulation and reducing stress. Some non-surgical options include medications to regulate hormones and minimize bleeding, as well as minimally invasive procedures like uterine artery embolization. These options often come with fewer risks and shorter recovery periods, making them appealing choices for many women.
- Diet modifications to support hormonal health
- Exercise routines to reduce symptoms
- Medications and minimally invasive procedures
Emerging Therapies and Future Directions
Emerging therapies for uterine fibroids focus on innovative pharmacologic agents and minimally invasive techniques that aim to improve outcomes. Personalized treatment strategies are becoming more prominent, allowing you to receive care tailored to your unique needs. These advancements hold promise for more effective and less invasive options in the future.
Novel Pharmacologic Agents
What new pharmacologic agents are on the horizon for treating uterine fibroids? Researchers are exploring targeted therapies that focus on hormonal modulation and fibroid biomarkers. These emerging agents aim to provide effective symptom relief with fewer side effects. They include selective progesterone receptor modulators and novel agents that influence local growth factors. These drugs could help regulate fibroid growth by altering hormonal signals or disrupting fibroid-specific pathways. Advances in identifying fibroid biomarkers enable more personalized treatments, improving outcomes. Future therapies may also target molecular mechanisms unique to fibroids, offering precision medicine approaches. As these agents develop, they promise to expand non-surgical options, reducing reliance on invasive procedures. You can expect a shift toward more tailored, hormone-based, and biomarker-guided treatments in the near future.
- Targeted hormonal modulation strategies
- Fibroid biomarker-based therapies
- Personalized, less invasive options
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Advances in minimally invasive techniques are transforming uterine fibroid treatment, offering effective options that reduce recovery time and procedural risks. Robot-assisted procedures allow precise removal or destruction of fibroids with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. These procedures often result in shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities. Ultrasound ablation, a non-invasive technique, uses focused ultrasound waves to target fibroids precisely, sparing healthy tissue and eliminating the need for incisions. Emerging technologies are making these options more accessible and efficient, expanding treatment possibilities beyond traditional surgery. As these minimally invasive methods evolve, you’ll have access to safer, less invasive treatments that improve outcomes and patient comfort while preserving uterine function.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
As research continues to evolve, personalized treatment strategies for uterine fibroids are becoming more sophisticated, allowing clinicians to tailor therapies to each patient’s unique anatomy and symptoms. You can now explore options that prioritize fertility preservation, ensuring you keep your reproductive potential intact. Emerging therapies offer promising alternatives to traditional surgery, focusing on less invasive approaches that target fibroids directly. These include medical treatments designed to reduce fibroid size and symptoms, as well as novel techniques that aim to minimize impact on fertility. Customizing your treatment plan means considering your goals, such as pregnancy or symptom relief, and choosing the most appropriate, least invasive option. This personalized approach helps improve outcomes while respecting your individual health priorities.
- Focus on fertility preservation with targeted therapies
- Explore alternative therapies that reduce invasiveness
- Tailor treatments based on your specific anatomy and goals
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Lifestyle Changes Prevent Uterine Fibroids?
While lifestyle changes can’t guarantee prevention, they may help reduce your risk of uterine fibroids. You should focus on diet modifications, like eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limiting red meat and processed foods. Incorporate regular exercise routines to maintain a healthy weight and improve hormonal balance. These steps can support overall reproductive health, potentially lowering your chances of developing fibroids over time.
Are There Natural Remedies to Reduce Fibroid Size?
You might wonder if natural remedies can reduce fibroid size. While there’s limited scientific proof, some herbal supplements like green tea extract and dietary adjustments focusing on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may support overall health. These approaches could help balance hormones and improve symptoms. Remember, consult your healthcare provider before trying herbal supplements or significant dietary changes to guarantee safety and effectiveness for your specific situation.
How Do Fibroids Affect Fertility and Pregnancy?
Fibroids can impact your fertility and pregnancy by causing hormonal influence that affects your reproductive system. They may interfere with implantation, block fallopian tubes, or distort the uterus, making conception harder. During pregnancy, fibroid growth can lead to complications like pain, preterm birth, or abnormal fetal positioning. Understanding how fibroids affect fertility helps you seek appropriate treatment options to improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
What Are the Long-Term Risks of Non-Surgical Treatments?
You should consider that non-surgical treatments like hormonal therapy can effectively manage fibroids, but they may come with long-term risks. Hormonal therapy can cause side effects such as bone density loss or hormonal imbalances over time. Additionally, fibroid recurrence is common once treatment stops, meaning you might need repeated therapies. It’s essential to weigh these risks with your healthcare provider to decide the best approach for your long-term health.
Are There Genetic Tests to Predict Fibroid Development?
They say knowledge is power, so it’s smart to ask if genetic tests can predict fibroid development. While research on genetic markers and predictive testing is ongoing, no definitive tests currently exist for individual risk. Scientists are exploring how certain gene variations may signal susceptibility, but it’s not yet routine. Keep informed and consult your healthcare provider to understand your personal risk factors better.
Conclusion
Understanding uterine fibroids is like charting a complex maze—you need to know the paths, influences, and options available. With non-surgical treatments, you gain more control, like steering a boat through calm waters instead of battling storms. By staying informed about the causes and latest therapies, you can make empowered decisions for your health. Remember, managing fibroids is a journey, and with the right knowledge, you’ll find your way to a better quality of life.









